 إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه
إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه احفظ. احمِ. استمتع.
 إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه
إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه  جدول المحتويات
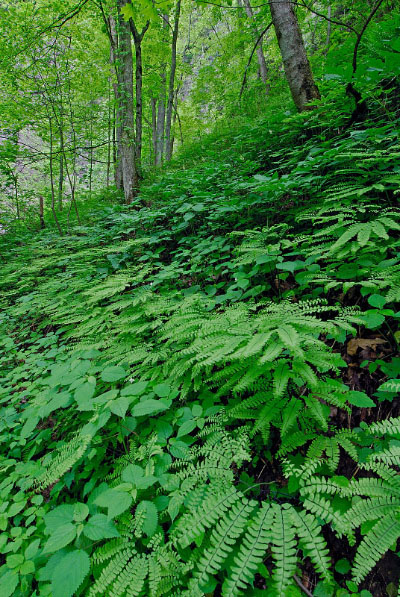
جدول المحتوياتغابات ريتش كوف
The mixed hardwood forests of this group occupy fertile, mesic, mountain-slope habitats at elevations ranging from about 300 m (1,000 ft) commonly to 1,100 m (3,600 ft), and occasionally higher. Distributed locally throughout western Virginia, these forests are strongly associated with moist, sheltered, landforms (i.e., coves, ravines, and concave lower slopes). Soils may be weathered from various substrates but are generally moderately acidic to moderately alkaline, with high base saturation. In these habitats, soil fertility appears to be strongly correlated with high base cation levels (particularly calcium, magnesium, and manganese) rather than with high pH, and higher-elevation sites often have soils with surprisingly low pH. Characteristic trees include sugar maple (Acer saccharum), basswoods (Tilia americana var. americana and var. heterophylla), white ash (Fraxinus americana), tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera), bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) and yellow buckeye (Aesculus flava); chiefly south of the James River). Herbaceous growth is lush with spring ephemerals and leafy, shade-tolerant forbs such as blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), yellow jewelweed (Impatiens pallida), large-flowered trillium (Trillium grandiflorum), wood-nettle (Laportea canadensis), common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa), sweet cicely (Osmorhiza claytonii), Virginia waterleaf (Hydrophyllum virginianum), large-leaf waterleaf (Hydrophyllum macrophyllum), large-flowered bellwort (Uvularia grandiflora), red trillium (Trillium erectum), yellow violets (Viola pubescens and Viola eriocarpa), white baneberry (Actaea pachypoda), two-leaved miterwort (Mitella diphylla), goat's-beard (Aruncus dioicus var. dioicus,), yellow mandarin (Prosartes lanuginosa), showy skullcap (Scutellaria serrata), eastern blue-eyed-mary (Collinsia verna), Guyandotte beauty (Synandra hispidula), glade fern (Homalosorus pycnocarpos), and many others. Compositional variation related to substrate and elevation is complex but the group partitions convincingly into several major community types. The principal threats to rich cove forests are logging and invasion by shade-tolerant, non-native weeds, especially garlic-mustard (Alliaria petiolata). The frequent to common white ash component of these communities is undergoing widespread mortality from Emerald Ash Borer outbreaks.
تتميز غابات الكهوف الغنية والغابات المنحدرة عن الغابات المتوسطة الأساسية المماثلة بتوزيعها المحدود والأكثر ارتفاعاً في الجبال؛ وتواجدها على ارتفاعات أعلى؛ وتكوينها الزهري الذي يتميز بعدد من الأنواع الآبالاشية المرتفعة في المقام الأول.
المراجع: كولينج وراوينسكي (1999)، فليمينج (1999)، فليمينج وكولينج (2001)، فليمينج ومورهيد (1996)، فليمينج ومورهيد (2000)، جونسون ووير (1982)، أولسون وهوب (1986)، راوينسكي وآخرون (1994)، راوينسكي وآخرون (1996)، راينهارت ووير (1984).
انقر هنا لمزيد من الصور لهذه المجموعة المجتمعية البيئية.

ويستند تصنيف هذه المجموعة على تحليل 119 عينة من قطع الأراضي التي تم أخذ عينات منها في 34 مقاطعات فرجينيا (الشكل 1). كما تم تحليل معظم قطع الأراضي في العديد من جهود التصنيف الإقليمية المتعددة الولايات لصالح دائرة المتنزهات الوطنية (على سبيل المثال، مشاريع رسم خرائط الغطاء النباتي في منطقة العاصمة الوطنية ودرب الأبالاش). هناك حاجة إلى جمع بعض البيانات الإضافية لتحديد النطاقات الجغرافية الكاملة داخل الولاية للأنواع الأربعة المصنفة. انقر على أي رمز من رموز CEGL المميزة أدناه لعرض وصف USNVC العالمي المقدم من مستكشف خدمة الطبيعة.

 قم بتنزيل جدول بيانات لإحصائيات ملخص التركيب لكل نوع من أنواع المجتمعات المدرجة أدناه.
قم بتنزيل جدول بيانات لإحصائيات ملخص التركيب لكل نوع من أنواع المجتمعات المدرجة أدناه.