 إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه
إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه احفظ. احمِ. استمتع.
 إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه
إدارة الحفاظ على البيئة والترفيه  جدول المحتويات
جدول المحتوياتغابات مونتاني الجافة والجافة-المتوسطة الجافة الجيرية
تغطي هذه المجموعة في المقام الأول غابات الجبال الجبلية وغابات الأخشاب الصلبة المختلطة التي تحتوي على عنصر كبير من أشجار البلوط، وتوجد على الحجر الجيري والدولوستون وأقل تواتراً على الصخور الصخرية الجيرية والطميية والرملية. تحتل المجتمعات في هذه المجموعة المنحدرات والقمم شبه الجافة إلى حد ما ذات الجوانب المختلفة والتربة الخصبة. "تنفصل أنواع المجتمعات المصنفة على طول تدرجات متقاطعة من الجغرافيا ورطوبة التربة وعمق التربة والجانب، وتنقسم تقريبًا إلى" الجاف و "مجموعات" الجافة - المتوسطة .
Dry calcareous forests occur on subxeric to xeric, fertile habitats over carbonate formations of limestone and dolostone, or very rarely highly calcareous siltstone or shale. Habitats are steep, usually rocky, south- to west-facing slopes at elevations from < 300 to 900 m (< 1,000 to 2,900 ft). Soils vary from circumneutral to moderately alkaline and have high calcium levels. Confined in Virginia to the mountains, these communities are most frequent and extensive in the Ridge and Valley, but occur locally in both the Blue Ridge and Cumberland Mountains. Tree canopies vary from nearly closed to quite open and woodland-like. Overstory mixtures of chinquapin oak (Quercus muehlenbergii), sugar maple (Acer saccharum), black maple (Acer nigrum), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), white oak (Quercus alba), Shumard oak (Quercus shumardii), white ash (Fraxinus americana) and blue ash (Fraxinus quadrangulata, extreme southwest Virginia only) are typical. These forests and woodlands share many understory and herbaceous plants with the Piedmont / Mountain Basic Woodlands group and are similarly species-rich. A few of the taxa that are confined to or most important in the limestone and dolostone communities include Carolina buckthorn (Frangula caroliniana), round-leaved ragwort (Packera obovata), robin's-plantain (Erigeron pulchellus var. pulchellus), American beakgrain (Diarrhena americana), slender muhly (Muhlenbergia tenuiflora), black-seed ricegrass (Patis racemosa), limestone purple sedge (Carex purpurifera, in extreme southwestern Virginia only), hairy sunflower (Helianthus hirsutus), small-headed sunflower (Helianthus microcephalus), northern leatherflower (Clematis viorna), and white death-camas (Anticlea glauca). Logging and fire exclusion are probably the biggest threats to dry calcareous forests.

Dry-mesic calcareous forests occur in deeper soils of valley sideslopes, lower mountain slopes, gentle crests, and ravines up to about 1,150 m (3,800 ft) elevation. Forests of this group are widely distributed in the Ridge and Valley province, more local in the Cumberland Mountains, and rare in the northern Piedmont Triassic Basin. Mixtures of sugar maple (Acer saccharum), black maple (Acer nigrum) , chinquapin oak (Quercus muehlenbergii), white oak (Quercus alba), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), black oak (Quercus velutina), white ash (Fraxinus americana), and hickories (Carya spp.) are typical. A distinctive variant is co-dominated by eastern white-cedar (Thuja occidentalis), usually in association with eastern white pine (Pinus strobus), eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis), and hardwoods. Tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera) is most abundant as an invader of logged stands. Understory and herbaceous vegetation varies from sparse to lush (especially on limestone sites), but is generally dominated by species characteristic of submesic soil moisture conditions, such as white snakeroot (Ageratina altissima var. altissima), hog-peanut (Amphicarpaea bracteata), common eastern bromegrass (Bromus pubescens), sharp-lobed hepatica (Hepatica acutiloba), and common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa).
يمكن تمييز الغابات الجافة - الجيرية الجافة - المتوسطة بسهولة عن غابات الكهوف والمنحدرات الغنية أو الغابات المتوسطة الأساسية من خلال وجودها في مواقع أقل حماية وغياب الأعشاب المتوسطة البارزة مثل الكوهوش الأزرق(Caulophyllum thalictroides)، أو الأوراق المائية عريضة الأوراق(Hydrophyllum canadense)، أو نبات القراص الخشبي(Laportea canadensis). وقد تم قطع أو تدمير العديد من الغابات الجيرية الجافة والوسطى بشكل كبير لأغراض الزراعة. في بعض الحالات، يبدو أن الغابات ناتجة عن غزو غابات البلوط والجوز من قبل أنواع أكثر اعتدالاً (خاصة القيقب السكري)، على الأرجح نتيجة لاستبعاد الحرائق على المدى الطويل. يعاني الرماد الأبيض، وهو شجر شائع جدًا في الغابات الجافة والجافة الجافة والوسطى الجافة على حد سواء، من وفيات كبيرة حاليًا نتيجة لتفشي حفار الرماد الزمردي.
المراجع: فليمنج (1999)، فليمنج وكولينج (2001)، فليمنج ومورهيد (1996)، فليمنج ومورهيد (2000)، روينسكي وآخرون (1996).انقر هنا لمزيد من الصور لهذه المجموعة المجتمعية البيئية.
 © دى سى آر دى إن إتشه، غاري ب. فليمنغ
© دى سى آر دى إن إتشه، غاري ب. فليمنغ
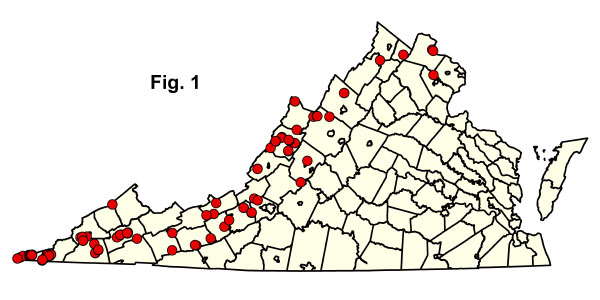
يتم دعم سبعة أنواع من المجتمعات المحلية من خلال 102 عينات مؤامرة كمية (الشكل 1 ). إن تصنيف معظم الوحدات قوي إلى حد ما، لكن التوزيع الكامل وحالة الأنواع الثلاثة المعروفة فقط من جبال كمبرلاند وجنوب ريدج والوادي غير واضح بعد ويحتاج إلى جرد إضافي. انقر على أي رمز من رموز CEGL المميزة أدناه لعرض وصف USNVC العالمي المقدم من مستكشف خدمة الطبيعة.
 قم بتنزيل جدول بيانات لإحصائيات ملخص التركيب لكل نوع من أنواع المجتمعات المدرجة أدناه.
قم بتنزيل جدول بيانات لإحصائيات ملخص التركيب لكل نوع من أنواع المجتمعات المدرجة أدناه.